For a prolonged period, Google has been changing title hyperlinks. The business started in 2014 to modify a title to reflect the inquiry (to a certain extent). This post discusses when Google’s title change goes wrong.
This is significant since Google would subsequently utilize these prior behaviors as precedence for its current approach, an explanation that several SEOs believed was deceptive given the extent and significance of the alterations.
See also: Why You Shouldn’t Be Creating Links To Your Site
Contents
Observing The Modifications In The Google SERP Title Tag
When Google’s Title Change Goes Wrong and Google disclosed modifications to its SERP page title generating method. SEOs have been scurrying to assess the effect and make appropriate adjustments to their strategy. Although several organizations witnessed minor adjustments to their title tags, few major exceptions were.

A group, in general, observed a significant change to the headline hyperlink on their MarTech objective website (the title of a search result in Google Search).
The SERP headline was altered to “MarTech is Marketing Logo,” taken from the primary logo alt content on their MarTech webpage. Although the actual title hyperlink was their preferred title. Google decided to present a snippet of alt text that provides no meaning and fails to entice users to explore.
Examining The Variations In Clicks And Click-through-rate (CTR)
The majority of the MarTech SERP title modifications they observed were minor. Consequently, their visits, views, and CTR figures have remained consistent in recent months.
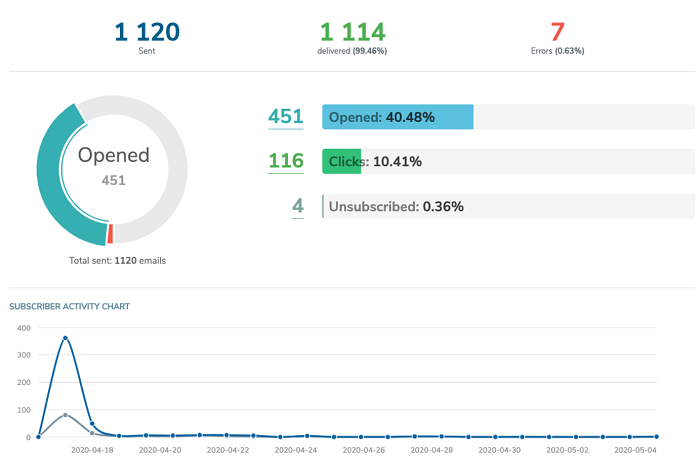
They evaluated the page’s November outcomes to its October outcomes, understanding the SERP title modification occurred between October 27 and November 1. The overall number of views on the website dropped from 2,301 to 1,500, and the overall CTR dropped from 3.1% to 2%.
The overall number of engagements increased to 75,427, with the overall rank remaining at 12.7. This suggests that the SERP title modification had little impact on accessibility or ranks (as Google claimed) but significantly negatively impacted people’s willingness to tap on the results.
The SERP title changes had a negative impact on the site’s traffic, and they had to seek a solution.
See also: Google Title Tag Update Casualties Lose Search Traffic
Taking Action To Modify The Headline Of The SERP
The very last thing the site owners intended to do was sit tight for Google to alter the title by itself, and they decided to take measures immediately. Following are some of the strategies they used:
1. Refresh The Webpage And Submit It Again
They resubmitted the webpage to Google using Search Console right away. Although it wasn’t expected to impact much, there was still the possibility that it could aid crawlers in detecting components on the webpage they’d overlooked, such as the heading tag in this instance.
2. The Title Tag Should Be Updated
The site operators performed a change after it seemed that the algorithm had a problem with the selected tag. They were cautious not to change it entirely; “What is MarTech?… “Marketing is MarTech.”
This modification made the subject of the webpage more prominent, which they thought Google would detect.
3. Include Internal Links That Are Relevant To The Topic
Although the webpage previously had a lot of internal hyperlinks leading to it. They sought to make sure Google had enough information. To inform the crawlers what the website was regarding. They inserted more hyperlinks with contextual title tags to the page — keyword phrases like “what is martech,” “martech is marketing,” or even “martech.”
4. Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) Should Be Monitored
They watched their title hyperlink to determine if the alterations had any effect. Each week or two, they would redo the procedures.


